Do you use varied tactics in both defensive and offensive strategies? Regardless of the excellence of your perimeter defenses, there are possibilities that cybercriminals will infiltrate your network.
Deception technology will waste their time exploring planted assets while you set them up in a trap.
Unlike legacy detection technologies that rely on signatures or behaviors/heuristics, this lures cyber criminals into irresistible traps and reveals their behavior.
This modern cybersecurity technique helps defender teams gain the intelligence (insight into attackers’ motives and actions) to respond quickly and effectively.

At the core of this technology, defenders use decoys and traps that look like natural systems in the network to mislead attackers.
It will leave them believing they have a foothold in the network and, hence, reveal themselves.
By deploying these, threat deception can help organizations of all sizes and maturity levels identify attackers, their tools, and tactics.
In this blog post, you can discover how this technology is revolutionizing threat detection with low false-positive alerts, real-time detection, scalability, and customization.
Low False-Positive Alerts
A key challenge for most security teams is dealing with the volume of alerts they receive.
Too many false positives can overwhelm defenders and result in them missing threats as they weed through the noise.
This often happens because many point products and tools monitor identity, authentication, and activity and can generate a lot of alerts that are not necessarily threats but could be something as benign as someone mistyping an IP address.
Deception technology solutions reduce the amount of noise and false positives generated.
Rather than simply flagging anomalies, this technology uses lures and traps that mimic natural systems to identify attackers and alert security.
Interesting Fact:
According to the recent research by PurpleSec, cybercrime increased by 600% during the epidemic.
For example, using fake Amazon S3 buckets containing the company’s name can reliably identify reconnaissance and lateral movement.
At the same time, decoy UAT/testbed servers and webmail systems can uncover spear-phished credentials or identify compromised users.
More advanced deployments include sink-hole servers that report attacker information to law enforcement officials.
This enables security teams to respond quickly and accurately, stopping attacks in their tracks or detecting them before they cause significant damage.
It also helps reduce Mean Time to Detection, a prominent business priority for most organizations.
Moreover, it can also reduce the cost of deploying and operating security technologies as it frees up person-hours that would otherwise be spent analyzing logs.
Real-time Threat Detection
The real-time detection of attacker activity is a game changer for any cybersecurity program.
This means fewer unwanted logs processed and analyzed by firewalls, fewer data that require analysis by SIEM tools, and more time for SOC analysts to focus on threat hunting.
Cyber deception complements other security controls by detecting discovery, lateral movement, privilege escalation, and collection activities that are hard to see with point solutions.

Statistics:
Recently, statistics have shown that the global deception technology market is estimated around $2.54 billion in 2023 at a CAGR of 15.5%.
But, by 2027, its market size is predicted to grow by $4.50 billion at a CAGR of 15.4%.
It also muddies the attack surface, which helps to reduce the attacker’s dwell time.
Unlike traditional behavior analysis, which triggers many false positives and lags in time for detection, deception creates a zero-activity baseline that only alerts when an attacker interacts with the decoy assets.
This enables IT to quickly sift through the attacker’s engagement data and determine their intent, such as surveillance, reconnaissance, exploitation, or lateral movement.
Forward-leaning, large-security-team-type organizations use deception to augment their security stack to address gaps in their detect, know, and respond capabilities. Their needs include:
- Deployment scalability.
- Low false-positive alerts.
- Integration with threat-hunting or response technologies that they already have in place.
This market segment has led the way for deception to be adopted more broadly.
Fraud is also becoming increasingly used by mid-market CISOs who want to move the needle on their detect, know, and respond metrics.
However, they often need more resources and budgets that limit the number of threat detection capabilities they can deploy.
Scalability
With security threats multiplying and threatening the corporate network at ever-increasing rates, IT teams can’t afford to spend time on false positives that can lead to missed attacks.
Many traditional detection and prevention tools rely on signatures or susceptible machine learning algorithms that generate false alerts.
This technology can provide the breadcrumbs attackers need without bogging down security systems, making it possible to detect threats more quickly and reduce the risk of false positives.
Also, it can be deployed throughout the enterprise to misdirect adversaries as they attempt to gain a foothold in the system.
They can create decoy assets on endpoints, networks, or application layers.
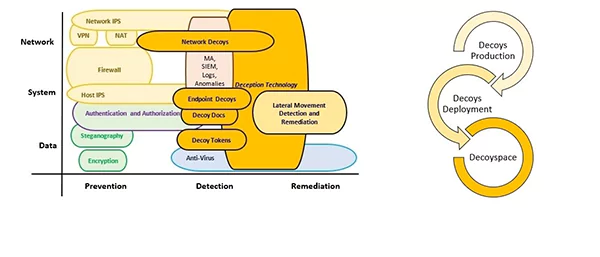
They can even be incorporated within existing data stores to lure attackers into traps that are difficult to break.
The decoys can be manipulated to look like tangible, valuable assets that attackers might target, including fault-finding business applications and servers.
By increasing the cost of an attack, these technologies can decrease the time attackers stay on an organization’s network and increase the number of detections they can make.
As a result, organizations can dramatically improve their incident response times.
Customization
Deception technologies allow security teams to create highly targeted bait and lures, such as fake cloud VMs, data centers, internal applications, etc.
This enables security teams to target specific attack objectives – such as ransomware, lateral movement, and even man-in-the-middle attacks – without alerting the tangible assets on the network.
This allows CISOs to create playbooks targeting particular attacks and attackers.
Do You Know?:
With the continuous use of deception technology, expenses have been reduced by up to 51%, resulting in an average savings of $75 per compromised record.
For example, less mature organizations can leverage it to identify insider threats by deploying fake UAT and staging environments or fake login portals.
The threat intelligence generated by these deception deployments reveals stealthy attacker activities, often evading detection by existing technologies.
The granular threat intelligence from its deployments also helps qualify medium or warm alerts generated by other security platforms, such as UEBA systems.
In doing so, deception solutions can help to reduce the ‘noise’ and ‘false positives’ that overwhelm security teams with too many false positive alerts.
With fewer and higher-confidence alerts, these technology solutions enable security teams to study attacker behavior more closely.
This can reveal TTPs and fingerprint attackers, decreasing an attack’s Mean Time to Know (MTTK). What is a flooded battery? This, in turn, can significantly improve the security team’s response capabilities and accelerate incident handling times.
This is especially vital as attacker dwell times on networks continue to increase.
Conclusion
It is evident that the adoption of deception technology solutions marks a significant shift in the realm of cybersecurity. It brings new ways for proactive and effective threat detection.
As you can see, its abilities provide low false-positive alerts, real-time threat detection, scalability, and customization capabilities. However, it provides an advantage over attackers by providing early and accurate detection.
With its tactics (decoy systems and content), this technology contributes to reducing Mean Time to Detection and improving incident handling times.